Be on the Alert for Aurora Sunday and Monday Nights
/The NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center has issued a watch for a Geomagnetic Storm Category G2. This means that places as far south as New York could see aurora on Sunday and Monday nights. Excerpt from the alert issued on 2020 Sep 27 2045 UTC:
Highest Storm Level Predicted by Day:Sep 28: G2 (Moderate) Sep 29: G2 (Moderate) Sep 30: G1 (Minor)
THIS SUPERSEDES ANY/ALL PRIOR WATCHES IN EFFECT
NOAA Space Weather Scale descriptions can be found at
www.swpc.noaa.gov/noaa-scales-explanation
Potential Impacts: Area of impact primarily poleward of 55 degrees Geomagnetic Latitude.
Induced Currents - Power grid fluctuations can occur. High-latitude power systems may experience voltage alarms.
Spacecraft - Satellite orientation irregularities may occur; increased drag on low Earth-orbit satellites is possible.
Radio - HF (high frequency) radio propagation can fade at higher latitudes.
Aurora - Aurora may be seen as low as New York to Wisconsin to Washington state.
UPDATE: The latest watch as of
Issue Time: 2020 Sep 29 1556 UTC
WATCH: Geomagnetic Storm Category G1 Predicted
Highest Storm Level Predicted by Day:
Sep 29: G1 (Minor) Sep 30: G1 (Minor) Oct 01: None (Below G1)
THIS SUPERSEDES ANY/ALL PRIOR WATCHES IN EFFECT
Comment: Decreasing max threshold potential from G2 to G1 to be consistent with activity as the storm progresses and wanes
NOAA Space Weather Scale descriptions can be found at
www.swpc.noaa.gov/noaa-scales-explanation
Potential Impacts: Area of impact primarily poleward of 60 degrees Geomagnetic Latitude.
Induced Currents - Weak power grid fluctuations can occur.
Spacecraft - Minor impact on satellite operations possible.
Aurora - Aurora may be visible at high latitudes, i.e., northern tier of the U.S. such as northern Michigan and Maine.The two main factors on whether or not you can see aurora on any given night are the level of geomagnetic activity and where you are located. Of course weather and light pollution will also affect your ability to see aurora. More tips for viewing aurora can be found at the NOAA site.
Here are some forecasts that will help:
The OVATION Auroral Forecast from NOAA below shows probability of visible aurora at the current time. Be sure to reload if the image is not current. Day and night (dark) are indicated as well on the map to help you determine if the time is current.
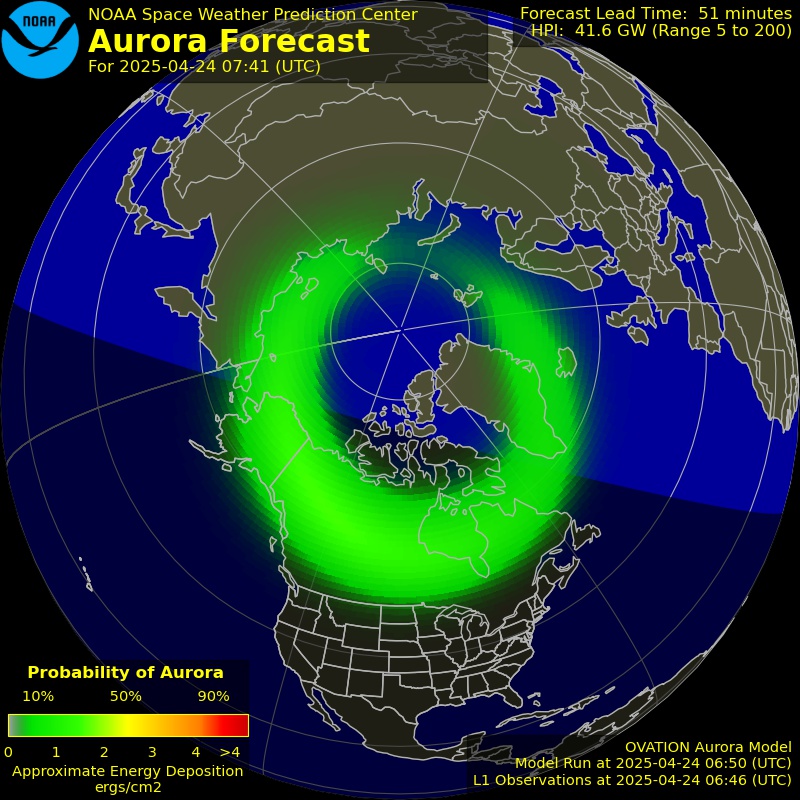
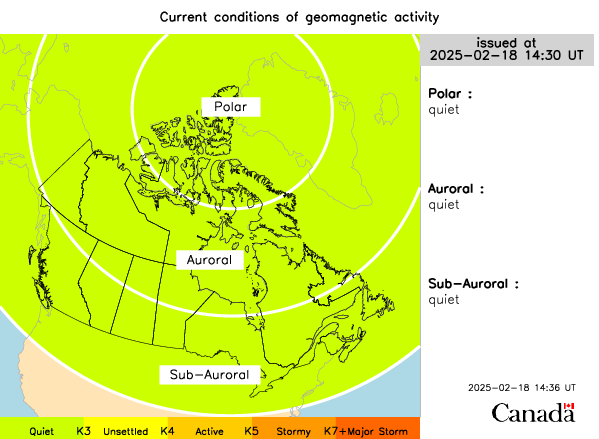
Space Weather Canada also issues Regional Magnetic Conditions and Forecasts and has regional specfic forecasts. Below is the current conditions of geomagnetic activity. The higher the K value the better chance of seeing aurora.
The Space Weather Gallery has some stunning photos and particularly these “Pinkest of all pinks (Aurora)” photos from Markus Varik in Norway. Pink auroras are rare and occur when particles reach lower levels of the Earth’s atmosphere. See spaceweather.com for further information.
We will update this page as new information becomes available.



