Looking Back on Canada's Costliest Winter Disaster: The Ice Storm of January 1998
/As Canadians rang in the New Year in January 1998, millions were unaware that in only a few days, they’d be caught in the middle of the costliest natural disaster in Canadian history. This is a record that stood for over 18 years, until the Fort McMurray fire of 2016. Nevertheless, it remains the most expensive winter disaster Canada has ever seen.
A 40,000km² area that covered Eastern Ontario and Upstate New York, up the St Lawrence Valley through Montreal, into the Eastern Townships of Quebec and across Maine into New Brunswick was coated in up to 100mm of ice that fell as freezing rain from the 5th until the 10th of January 1998. Light freezing rain was even experienced in Waterloo Region, to the west of Toronto and extended as far east as Western Nova Scotia. It’s important to note that this wasn’t a single storm, but rather a series of three smaller storms that produced freezing rain and ice pellets over an almost week-long period.
The Christmas Break in December 1997 was cold and snowy across much of Southern Ontario and Quebec so it was refreshing when New Year’s Day brought mild temperatures and sunshine to the region. However, a concerning weather pattern was shaping up.
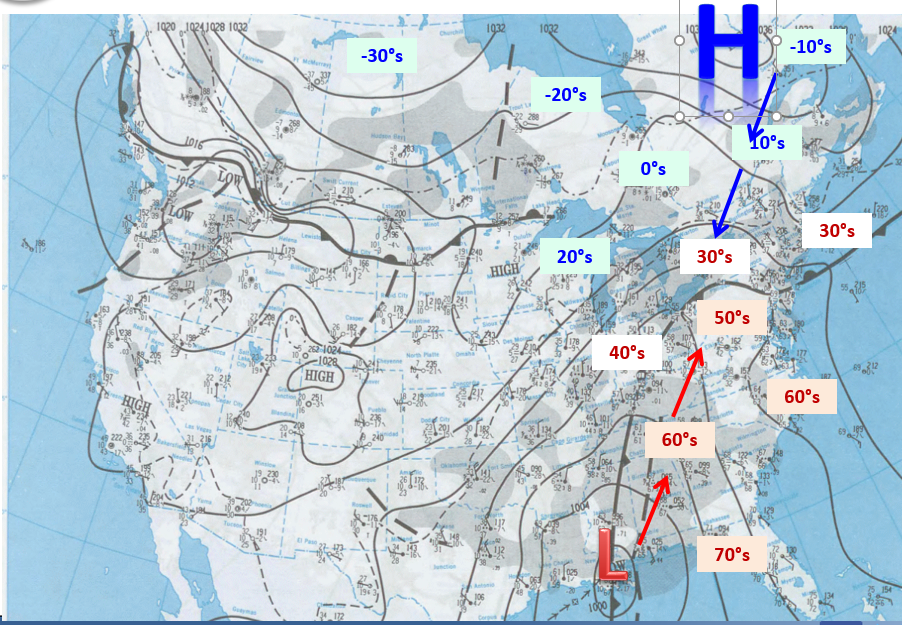
The surface chart from January 7th, 1998 showing the positions of the high and low pressure, areas of precipitations (shaded in darker grey) and the temperatures in degrees Fahrenheit, courtesy of the National Weather Service.
In the coming days, a strong high pressure area settled over Northern Quebec, which forced cold Arctic air southwards, while multiple low pressure systems from the south funnelled warm, moist air northwards. When the two air masses collided, the warm air rose above the cold air and then when the rain fell from the warm air mass, it froze on contact with surfaces at ground-level where the air was much colder.
This is what typically occurs in freezing rain events, but what made this different was the persistent flow of warm, moist air straight from the Gulf of Mexico continuing over several days, turning this into a prolonged event.
Temperature Profiles and the formation of different precipitation types.
The moist Gulf air arrived first, on January 4th, and brought mild temperatures and light rain to most of the impacted region. The next day, the Arctic air moved in and settled below the warmer air mass, bringing surface temperatures back below freezing and resulting in the transition from rain to freezing rain.
The high pressure continued to build over Northern Quebec throughout the following days, which maintained the flow of Arctic air, while the moist Gulf air surged northward in three distinct rounds of precipitation. According to Environment Canada, these three waves were: from 6:00pm on January 5th to 8:00am on January 6th, from 6:00pm on January 7th to 8:00am on January 8th, and from the morning of January 8th until the morning of January 9th.
Overall, an average of 50-70mm of freezing rain fell across the entire region. However, an area later called the “Triangle of Darkness”, between the towns of Saint-Hyacinthe, Granby, and Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu, was hit the hardest, with more than 100mm of ice accretion.
Total Ice Accretion amounts from the January 1998 Ice Storm, courtesy of the National Weather Service.
Map of the total Ice Accretion from the January 1998 Ice Storm, with a Focus on Eastern Ontario and Southern Quebec, Courtesy of Hydro Quebec.
It didn’t take long for the effects of the ice buildup to be felt. Transportation quickly came to a halt as roads and sidewalks became skating rinks and vehicles were completely encased in ice.
After 10-20mm of freezing rain from the first round of precipitation, tree branches were already bending under the weight of the ice and as more freezing rain fell, the branches broke and entire trees toppled. Residents reported that the continuous sounds of ice-covered trees and branches breaking and falling was akin to gunshots. No definitive number was ever established, but it is estimated that millions of trees fell as a result of this storm.
It was also early on in the event that the strain on the power grid was felt and it only got worse as the freezing rain continued. Transmission lines sagged with the extra weight and short circuits caused by ground wires sagging and touching live wires tripped switches. Fasteners responsible for holding these lines were unable to handle the extra weight from all of the ice and snapped, while entire hydro poles and large towers eventually collapsed.
On top of all of this, transformers were damaged and caught fire, leading to further destruction of the hydro distribution system. Overall, 1,000 hydro pylons crumpled and at least 30,000 hydro poles were destroyed, plunging over 4 million people in Ontario, Quebec, and New Brunswick into darkness.
A montreal street covered in ice from the January 1998 ice storm, courtesy of Hydro Quebec.
While most people who were impacted by the ice storm were in urban areas, two groups in particular were significantly impacted in rural regions.
The stretch of the country hit by the ice storm was home to roughly 25% of all dairy cows in Canada and farmers encountered considerable challenges with the loss of power. Many cows got sick when it became difficult to feed them, milk them, and keep them warm.
With the lack of power at processing plants, over 10 million litres of milk, worth roughly $5 million, had to be dumped. Hydro Quebec reports that it was able to provide generators to many cattle farmers in the province, but unfortunately an estimated 300,000 farm animals across the entire region died in the cold.
Quebec’s maple syrup industry also took a massive hit with the ice storm. More than 20% of syrup-producing trees were damaged or destroyed as branches fell or large pieces of the trees splintered off, and equipment collapsed under the weight of the ice. Some syrup producers had their entire sugar bushes destroyed and while trees and the industry have mostly recovered, some scars still remain.
A convoy of troops deployed from Petawawa en Route to aid victims of the ice storm, taken January 9th, 1998, Courtesy of Veterans Affairs Canada.
On January 7th, at the peak of the ice storm, the Provincial Governments of Ontario, Quebec, and New Brunswick appealed to the Federal Government for assistance. The next day, 15,000 members of the Canadian Armed Forces were deployed from 200 different units from across the country as part of Operation Recuperation, making this this largest peacetime deployment of troops in Canadian history.
Troops worked with hydro companies to help restore power, cleared tree limbs and other debris, evacuated residents, and provided shelter, food and medical care to victims. The Operation eventually concluded on February 28th, 1998.
Due to the sheer level of damage across such a large area, the cleanup of debris and restoration of power was not something that was going to occur overnight. Temperatures plummeted following the ice storm to -20°C, so staying warm was the number one concern in the aftermath.
Many people were able to stay with family and friends who still had power, but emergency shelters were set up and available for those with nowhere else to go. Approximately 600,000 people were temporarily displaced from their homes while crews worked to restore power.
Thankfully, hydro crews from across the country and the United States came to the aid of those in the disaster area. The power was restored to many people in urban areas after a few days, but efforts took longer in rural communities, with roughly 700,000 people still without power three weeks after the storm.
The ice storm was a real testament to the sense of community as well as the welcoming and giving nature of Canadians. Many people came together to help clean up and provide food and shelter to those in need. Despite all this, the storm resulted in 945 injuries and 35 people sadly lost their lives.
On top of the human cost, the storm had a very large financial cost. The incredible amount of damage caused by this storm was estimated to have cost insurers $1.38 billion. Furthermore, entire cities were shut down and 2.6 million people in Ontario and Quebec, consisting of close to a fifth of the Canadian workforce, unable to get to work. The loss of productivity was over $1 billion and when added to insured damages and the over $2 billion it cost to repair utilities, the overall financial cost of the storm is estimated at $5.4 billion.
Further Reading:
https://canadiangeographic.ca/articles/lessons-learned-from-the-ice-storm-of-1998/
https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/montreal/ice-storm-1998-1.4469977
https://www.hydroquebec.com/ice-storm-1998/
https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/ice-storm-1998
https://www.veterans.gc.ca/en/remembrance/wars-and-conflicts/caf-operations/service-in-canada/ice-storm
https://www.weather.gov/btv/25th-Anniversary-of-the-Devastating-1998-Ice-Storm-in-the-Northeast