Intense Snow Squalls Return to Parts of Southern Ontario on Monday; Possible Deep Freeze for Late January
/⬇️ ZOOMED IN MAP CAN BE FOUND FURTHER DOWN ⬇️
The first half of January is almost behind us, and in Southern Ontario, the weather has shifted significantly compared to December. Colder temperatures have dominated, leading to several bouts of snow squall activity off Lake Huron and Georgian Bay. These events have primarily impacted regions southeast of the lakes.
The threat of snow squalls is set to return this week, with the heaviest snow expected east of Lake Huron and Georgian Bay. A predominant westerly flow will target areas such as Parry Sound, Bracebridge, Gravenhurst, and parts of Grey and Bruce counties. This pattern is reminiscent of what we experienced in early December, with heavy snow focused in the snowbelt regions east of Georgian Bay.
Snow squalls are forecasted to develop Monday afternoon and further intensify into the evening and overnight hours. Rapid snowfall accumulation and near-zero visibility are likely, especially late Monday into early Tuesday.
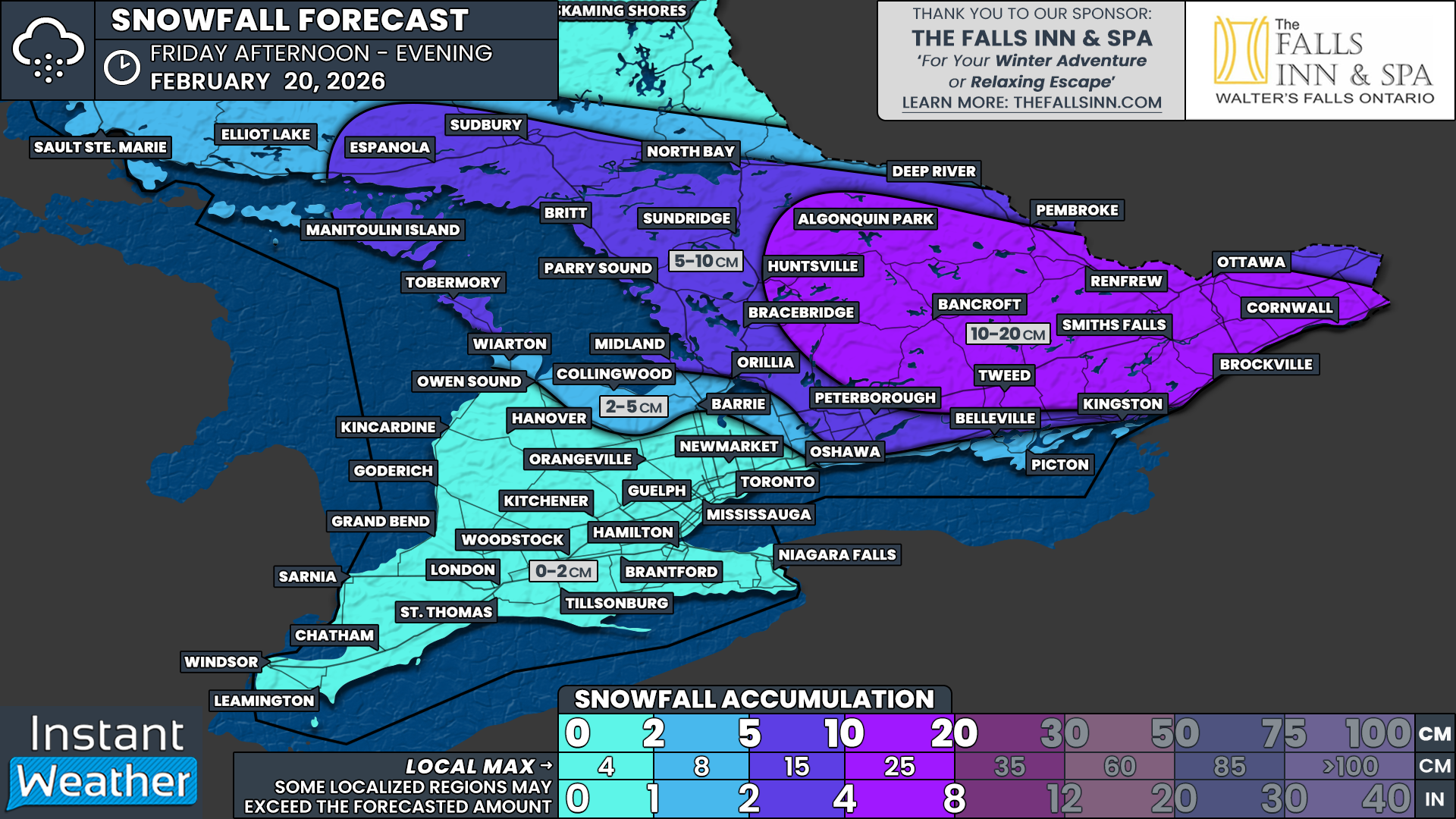
By the time the squall activity tapers off on Tuesday afternoon, some localized areas in the Muskoka and Parry Sound regions could see totals between 25 and 50 cm.
A brief reprieve from lake-effect snow is expected after Tuesday as milder air moves into Southern Ontario. However, another Arctic plunge is anticipated by early next week, potentially bringing some of the coldest air of the season.
Wind chills could make it feel like -30°C or even -40°C, especially in Central and Eastern Ontario!
This upcoming cold snap could also reignite intense lake-effect snow activity, with several rounds of squalls likely to impact the snowbelt regions throughout the rest of January.
BREAKING DOWN THE TIMING OF THE SQUALLS
Before the snow squalls begin Monday, a weak clipper system is forecasted to move across Southern Ontario late Sunday into early Monday morning. While this system will lack significant moisture, it may bring light snowfall of 2 to 5 cm in most areas, with localized pockets potentially reaching up to 5 cm.
HOURLY SNOWFALL RATE/intensity - MAP FROM WEATHERBELL
In the wake of the clipper, lake-effect snow is expected to ramp up east of Georgian Bay on Monday afternoon. Initially, the snow may be disorganized, spreading moderate to heavy snowfall across Muskoka and parts of Grey and Bruce counties.
HOURLY SNOWFALL RATE/intensity - MAP FROM WEATHERBELL
By Monday evening, forecast models indicate the formation of a more organized snow squall. This band is expected to stretch from the Bruce Peninsula across Georgian Bay and inland between MacTier and Parry Sound.
The squall could remain stationary overnight, leading to rapid snowfall accumulation at rates of 5 to 10 cm per hour.
Model projections differ slightly regarding the exact placement of the most intense squall. The American model places the heaviest snow over Parry Sound, Pointe au Baril, Sprucedale, and Burk’s Falls.
HOURLY SNOWFALL RATE/intensity - MAP FROM WEATHERBELL
Meanwhile, the Canadian model suggests the squall may shift south after midnight, targeting areas such as Port Carling, Rosseau, Port Sydney, and Bracebridge for the heaviest snowfall.
HOURLY SNOWFALL RATE/intensity - MAP FROM WEATHERBELL
Both models agree that the squall will gradually sink southward by late Tuesday morning, bringing heavy snow to northern Simcoe County, including Midland and Orillia.
However, there is uncertainty about the intensity and duration of the squall as it moves further south into Barrie.
HOURLY SNOWFALL RATE/intensity - MAP FROM WEATHERBELL
While Georgian Bay will see the most intense squalls, Lake Huron is also expected to generate less intense snow bands Monday evening into Tuesday morning. These bands could impact Owen Sound, Kincardine, and Hanover, with bursts of heavy snow.
As the wind shifts southward, areas like Goderich and London may briefly experience lake-effect snow Tuesday morning into the afternoon.
WHO COULD GET BURIED IN SNOW
As is typical with lake-effect snow, snowfall totals will vary widely depending on where the narrow bands persist. The highest accumulations are expected in Parry Sound, Rosseau, Port Carling, Port Sydney, Bracebridge, and Gravenhurst, where 25 to 50 cm of snow is possible by Tuesday afternoon.
In some areas, totals could exceed 50 cm if the squall remains stationary for an extended period.
Surrounding areas such as Midland, Washago, Coboconk, Minden, Huntsville, and Sprucedale may see snowfall totals of 15 to 25 cm.
The Grey-Bruce region, including Kincardine, Port Elgin, Wiarton, Lion’s Head, Tobermory, Owen Sound, Chatsworth, Hanover, and Meaford, is expected to receive 15 to 25 cm, with localized totals of 30 to 40 cm if squalls intensify.
Elsewhere in Central and Southwestern Ontario, snowfall amounts will range from 5 to 15 cm, combining accumulation from the weak clipper system and lake-effect snow. Most areas will see closer to 5 cm, with lake-effect zones reaching 10 to 15 cm.
Less than 5 cm is expected for the rest of Southern Ontario.
SNOW SQUALL WATCH ISSUED BY ENVIRONMENT CANADA
CURRENT ENVIRONMENT CANADA ALERTS AS OF SUNDAY EVENING
Environment Canada has issued snow squall watches for areas around Lake Huron, Georgian Bay, and Lake Superior.
The highest totals in these watches match our forecast, with 20 to 40 cm expected for Parry Sound and Muskoka and 15 to 25 cm for the Grey-Bruce region.
Northern Ontario, including Sault Ste. Marie and Manitoulin Island could see localized snowfall of 10 to 20 cm from Monday evening into Tuesday morning.
LOOKING AHEAD TO THE REST OF JANUARY
The persistence of lake-effect snow this far into January may seem unusual, but the Great Lakes remain relatively ice-free and warmer than usual due to a mild fall and warm start to winter. This provides ample moisture for snow squalls when Arctic air moves in.
ICE COVERAGE MAP AS OF JANUARY 11, 2025 - source: NOAA
Colder weather in recent weeks has helped cool the lakes and increased ice coverage, particularly in shallower areas like Lake Erie and the shorelines of Lake Huron and Georgian Bay.
Ice coverage has risen from 1% at the start of January to over 10% as of January 11.
TEMPERATURE ANOMALY - MAP FROM WEATHERBELL
Looking ahead, a significant Arctic blast is expected during the January 20–24 period, with temperatures 10 to 20 degrees below seasonal norms across much of Southern Canada and the northern U.S.
Southern Ontario could experience lows well below -20°C, potentially nearing -30°C in some areas. Wind chills could make it feel as cold as -35°C to -40°C, particularly in Central and Eastern Ontario.
This intense cold will likely bring additional snow squalls and accelerate ice formation on the Great Lakes. If current trends continue, lake-effect snow activity could diminish significantly by the end of the month as ice coverage increases, shutting off the moisture source for squalls.
For snowbelt residents weary of lake-effect snow, relief may finally be on the horizon!